Is UEFI required for Windows 11? This post shows clear details of UEFI and help users to successfully upgrade to Windows 11.
After Microsoft has released Windows 11 for more than one year, the biggest update--22H2 is coming. In the last year, many users are unsatisfied with many glitches and bugs in Windows 11, so many people want to know if the new update solves some bugs or not and what improvements have been done.
Although there are various changes in the new updates from the information of many tech websites, according to the official reports, the basic requirements of Windows 11 are still the same. And the UEFI boot mode is one of them.
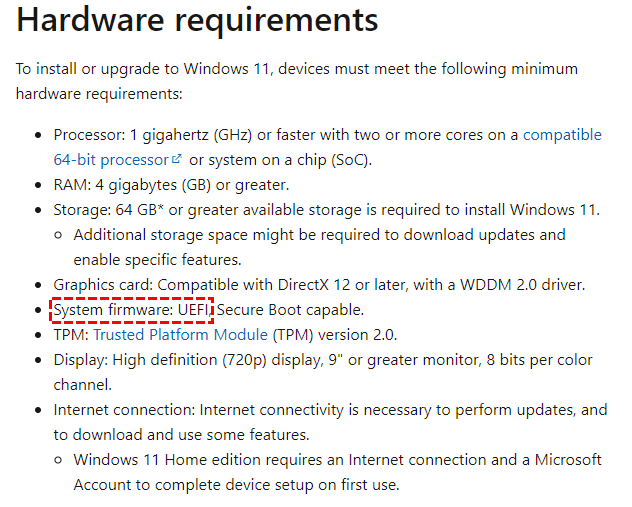
If you’re a PC technology amateur, you might have nothing to worry about, but, many users are still confused about BIOS and UEFI, MBR, and GPT. Therefore, we’ll introduce more details about these two groups.
1. What’re BIOS & UEFI?
BIOS: It’s the short of “Basic Input Output System”, which is a set of programs that are cured on a ROM chip on the motherboard of the computer. It stores the most important basic input and output programs of the computer, self-checking programs after power-on, and system self-starting programs.
The main function is to provide the most direct hardware settings and control for the computer and it is the first software loaded when a personal computer starts. This means when your PC boots up, the BIOS will activate the different components and ensure they’re operational to boot your OS.
UEFI: UEFI stands for “Unified Extensible Firmware Interface”. It is a PC system specification used to define the software interface between the operating system and the system firmware.
As the replacement of BIOS, it’s simple to operate and mouse-capable. And it also allows Windows to boot from a disk larger than 2TB (GPT disk). Some modern motherboards have supported both the old BIOS and the new UEFI.
2. What are MBR & GPT?
MBR and GPT are both partition methods.
MBR: MBR is short for “Master Boot Record”, considered the finest disc architecture of the twentieth century, is inextricably linked with HDD.
On the one hand, MBR only suits a hard drive with a capacity of up to 2TB. The additional part will not be recognized if MBR is used for a larger-capacity hard drive. On the other hand, it only enables partitioning the hard drive into 4 partitions.
GPT: GPT is the GUID partition table, a new partition table. The most obvious advantage of GPT is that it removes the constraint that MBR only handles up to 2T hard drives. Theoretically, GPT allows users to partition the hard disk into an infinite number of partitions.
What’s more, another big advantage of GPT partitions is to create different partitions for different data and at the same time create different permissions for different partitions. This ensures the security of the data in the disk.
3. BIOS + MBR VS UEFI + GPT
These 2 pictures show more details about BIOS + MBR and UEFI + GPT.
The BIOS + MBR mode supports more systems, but it has to deal with the limits of MBR, while the UEFI + GPT mode possesses perfect compatibility, larger capacity permission, and faster boot speed.
The combination of BIOS + MBR is workable but the system cannot be started. The BIOS can use the hard disk of the GPT partition table as the data disk, and the system must be a 64-bits system.
Motherboards manufactured in recent years support both BIOS and UEFI, and some of them have Legacy + UEFI boot mode. When the BIOS finds a Legacy-installed system, it enters the Legacy boot mode, if it identifies a UEFI-enabled machine, it will boot into UEFI mode.
If you don’t know what your PC is using, we’ll show how to check it how to check if your motherboard supports UEFI.
Step 1. Press “Win” + “R” at the same time, type “msinfo32” and hit “Enter” to open the System Information window.
Step 2. Find “BIOS Mode” in the window, if it shows “UEFI”, then you can upgrade your Windows 10 if this is the only issue that bothers you. If it shows “Legacy”, it only means your PC is running BIOS.
If your BIOS mode shows “Legacy”, that doesn’t mean the motherboard can’t support UEFI. You can check your motherboard name and manufacturer on the Internet to make sure whether it supports UEFI or not.
Since upgrading to Windows 11 requires a UEFI environment, you need to convert the MBR system disk to GPT before changing Legacy to UEFI. To make the conversion without losing data,
we recommend you a convenient tool to securely convert MBR disk to GPT disk AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional. It is a powerful disk and partition manager, whose “Convert to GPT Disk” function can convert your MBR disk to GPT disk and help you successfully change BIOS mode to UEFI mode. And it also has various pragmatic functions like migrating OS, moving installed programs without reinstalling, etc.
Step 1. Install and launch AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional. Right-click the system disk and choose “Convert to GPT”.
Step 2. Click “OK” to confirm your operation.
Step 3. Click on “Apply” to commit the pending operation.
And then the computer will finish the operation in WinPreOS mode.
After successfully converting MBR to GPT, you can change BIOS to UEFI.
Step 1. Start your computer and press the functional key (generally, it is F1, F2, F3, F10, or F12, ESC) to enter the firmware interface when you see the first screen. The functional key is different from computer to computer.
Step 2. Under the BOOT tab, choose the UEFI/BIOS Boot Mode, and change the Legacy to UEFI. Then save and exit the firmware interface.
When all is done, you can upgrade your Windows 10 to Windows 11.
Is UEFI required for Windows 11? The answer is yes. But with the help of AOMEI Partition Assistant, UEFI is no longer a hinder to the Windows 11 upgrade. You can convert MBR to GPT disk safely. This reliable software even has a “Win2go” feature, you can enjoy your own Windows 11 OS on any qualified computer. If you’re a Windows Server user, don’t worry, AOMEI Partition Assistant Server is designed for Server users.