You can learn how to check the speed of an SSD in two different ways in this tutorial. Whether checking sequential read speed SSD or random speed, it can be done easily.
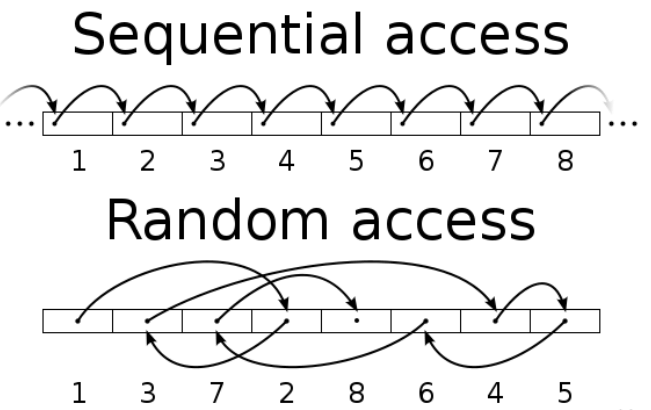
Sequential access and random access are how computers write or read data. Sequential access is when the computer reads or writes data sequentially from the beginning, and progresses step by step. Random access means that the computer can read or write data anywhere.
SSD sequential read speed is a relative concept of random read speed. Sequential read speed is the reading of contiguous blocks of data with a queue depth of 1 from adjacent locations on the surface of the device. Primarily used for benchmarking, speeds are usually measured in MBps. This access pattern is common when reading large files such as video, music, and images. When manufacturers refer to the speed of devices like flash drives, hard drives, and SSDs, they're referring to sequential speeds unless otherwise specified.
In SSD, when sequential data is written in sectors, SSD performs approximately 3.4 times faster, and in read sectors, SSD performs approximately 3.5 times to 5 times faster. Therefore, with the help of “sequential/random speed statistics”, users can easily calculate the performance of SSD/HDD. And make the computer run faster.
What is the sequential read speed of SSD has been introduced to you in the first part. However, do you know how to check the sequential read speed of SSD in your computer? Don’t worry, the following parts will provide two ways for you.
The easiest way to view the sequential read speed SDD is through the task manager, you can refer to the following steps:
Step 1. Enter “Task Manager” in the search bar and open it.
Step 2. Once opened, browse to the “Performance” option.
Step 3. Check the read and write speed of the SSD according to the list on the left, but this report only presents some basic information about the read/write speed of the SSD.
As you can see, you can only see some basic information about the SSD's sequential read speed from the Task Manager, it may not be enough to make you fully understand about SSD's speed.
For this, you can use AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional. This is a powerful and safe disk speed test tool that provides two speed test modes: Simple Mode and Expert Mode. It supports exporting test results.
If you want to know how to check sequential read speed SSD, please download the Demo version for a free trial!
Step 1. Install and launch it. In the top toolbar, choose "Test" > "Disk Speed Test".
Step 2. In this window, select the partition to be tested. Then select the test mode according to your needs. Simple Mode will only report the read and write speed of the selected SSD. “Pro Mode” presents more comprehensive results.
Step 3. In the “Pro Mode” window, you can change the default settings: Partition, Speed, Size, Tests Number, Duration(s), etc.
Step 4. After setting everything up, click “Start”.
If you're disappointed with your SSD's read and write speeds, you can take some measures to improve its performance.
The most common and efficient way is 4K alignment. SSD uses the smallest 4K sectors in the file system to save data. If the smallest 4K allocation unit is not always aligned with the 4K pages in the SSD, the performance of the SSD will suffer.
Warning: Please don’t defrag the SSD, because that will shorten the lifespan of the SSD.
Step 1. Install and run AOMEI Partition Assistant. Right-click the partition you want to align and select Advanced > Partition Alignment.
Step 2. In the pop-up window, select 4096 sectors from the given list and click OK.
Step 3. Click Apply > Proceed to execute the operation.
After reading this tutorial, I believe you already know how to check the sequential read speed of SSD. This post shows you two methods: Task Manager is a Windows built-in tool, but the reports it provides are sketchy. However, AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional provides the SSD speed test report that is more accurate and detailed.
Last but not least, AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional can do more about managing disk/partition, such as migrate OS to HDD/SSD, allocate free space from one drive to another, move installed programs to another drive, etc.